문제
1. entity 패키지를 만들고 다음과 같은 필드를 갖는 Friend 라는 엔티티 클래스를 생성한다.
id (int - PK, auto increment )
fname (String)
fage (Integer)
2. repository 패키지를 만들고 CRUD 가 가능한 FriendRepository 를 생성한다.
3. CRUD 기능을 점검하는 테스트 클래스 FriendTest를 생성하여 입력, 추출, 수정, 삭제 등을 테스트 한다. 또한 데이터가 3개 정도 남아 있게 한다.
4. controller 패키지에 FrindController를 생성한다.
- 친구 데이터의 명칭(URI)를 적당하게 정한다. → 자원에 대한 식별 가능한 이름
- 친구 데이터의 전체 리스트를 JSON 형식으로 리턴하는 메서드를 구현한다. (GET)
- ID 를 입력하면 해당 친구 데이터를 JSON 형식으로 리턴하는 메서드를 구현한다. (GET)
- 친구 이름을 입력하면 해당 친구 데이터를 JSON 형식으로 리턴하는 메서드를 구현한다.(GET)
- 클라이언트에서 JSON 형식으로 전달된 데이터를 Friend 테이블에 저장하는 메서드를 구현한다. 이 땐 ID 외의 데이터만 전달한다. (POST)
- 클라이언트에서 JSON 형식으로 전달된 데이터를 Friend 테이블에 저장하는 메서드를 구현한다. 이 때는 ID 도 전달해야 한다. (PUT)
- 클라이언트에서 전달된 ID 를 가지고 데이터를 삭제하는 메서드를 구현한다. (DELETE)
- 모든 응답은 ResponseEntity 를 사용한다.
- 전체 리스트 요청 : 응답 코드 200, 내용(없을 수도 있음)
- ID 로 친구 데이터 1개 요청 : 존재하면 200과 함께 친구 정보,존재하지 않으면 응답코드 404 와 함께 응답 헤더에 다음을 추가 BAD_ID : id값
- 입력 : 성공하면 응답코드 201(Created), 실패하면 500과 실패했다는 메시지
- 수정과 삭제 : 성공하면 205(Rest Content), 실패하면 500과 실패했다는 메시지
상태코드를 지정하여 응답할 때는 org.springframework.http.HttpStatus의 해당 상수를 사용한다.
FriendController 코드
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/friend")
public class FriendController {
@Autowired
FriendRepository friendR;
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<List<Friend>> list() {
// ResponseEntity<List<Friend>> entity = new ResponseEntity<>(friendR.findAll(), HttpStatus.OK);
// return entity;
// 빌더 이용
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(friendR.findAll());
// spring에서 내부적으로 .build()가 호출되기 때문에 명시적으로 호출하지않아도 됨
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Friend> getFriendById(@PathVariable int id) {
ResponseEntity<Friend> entity;
try {
Friend f = friendR.findById(id).get();
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(f, HttpStatus.OK);
}catch (Exception e){
HttpHeaders header = new HttpHeaders();
header.add("BAD_ID","id");
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(header, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
return entity;
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<String> register(@RequestBody Friend vo) {
ResponseEntity<String> entity;
try {
friendR.save(vo);
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.CREATED);
} catch (Exception e) {
entity = new ResponseEntity<>("실패했습니다.", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
return entity;
}
@PutMapping
public ResponseEntity<String> update(@RequestBody Friend vo) {
ResponseEntity<String> entity;
try {
Friend f = friendR.findById(vo.getId()).get();
f.setFage(vo.getFage());
f.setFname(vo.getFname());
friendR.save(f);
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.RESET_CONTENT);
} catch (Exception e) {
entity = new ResponseEntity<>("수정을 실패했습니다.", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
return entity;
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<String> delete(@PathVariable int id){
ResponseEntity<String> entity;
try{
Friend f = friendR.findById(id).get();
friendR.delete(f);
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.RESET_CONTENT);
}catch (Exception e){
entity = new ResponseEntity<>("삭제를 실패했습니다.", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
return entity;
}
}Friend.java 전체 코드
package springrest.exam.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@Entity
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class Friend {
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Id
private int id;
private String fname;
private Integer fage;
}
FriendRepository.java
package springrest.exam.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import springrest.exam.entity.Friend;
@Repository
public interface FriendRepository extends JpaRepository<Friend, Integer> {
}
FriendTest.java
package com.example.springedu2;
import jakarta.transaction.Transactional;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.MethodOrderer;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.TestMethodOrder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.jdbc.AutoConfigureTestDatabase;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.DataJpaTest;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import springrest.exam.entity.Friend;
import springrest.exam.repository.FriendRepository;
import java.util.List;
@AutoConfigureTestDatabase(replace = AutoConfigureTestDatabase.Replace.NONE)
@TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class)
@DataJpaTest
public class FriendTest {
@Autowired
FriendRepository friendR;
@Test
@Transactional
void list(){
List<Friend> list = friendR.findAll();
list.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
void save(){
Friend f;
for(int i = 0; i <2; i++){
f = new Friend();
f.setFage(1+i);
f.setFname("노키"+i);
friendR.save(f);
}
List<Friend> list = friendR.findAll();
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
@Transactional
void update(){
Friend f = friendR.findById(3).get();
f.setFname("수정테스트");
friendR.save(f);
List<Friend> list = friendR.findAll();
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
@Transactional
void delete(){
friendR.deleteById(3);
List<Friend> list = friendR.findAll();
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
친구 데이터의 전체 리스트를 JSON 형식으로 리턴하는 메서드를 구현한다. - GET 방식
첫 번째 방법
ResponseEntity<List<Friend>>타입의 entity를 생성한 뒤 Body에 FriendRepository의 findAll()을 호출한 결과를 담고 Header에는 HttpStatus.200을 담아서 return함
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<List<Friend>> list() {
ResponseEntity<List<Friend>> entity = new ResponseEntity<>(friendR.findAll(), HttpStatus.OK);
return entity;
}
두 번째 방법
Builder을 이용해서 ResponseEntity의 Body에 FriendRepository의 findAll()을 호출한 결과를 담고 Header에는 HttpStatus.200을 담아서 return함
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<List<Friend>> list() {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(friendR.findAll());
}
전체 리스트를 return해야 하기 때문에 @GetMapping을 사용
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/friend")
public class FriendController {
@Autowired
FriendRepository friendR;
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<List<Friend>> list() {
// 빌더 이용
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(friendR.findAll());
}
결과
친구 이름을 입력하면 해당 친구 데이터를 JSON 형식으로 리턴하는 메서드를 구현한다. – GET 방식
- @PathVariable을 사용해 파라미터로 오는 id를 받음(name이 동일하기 때문에 따로 이름을 설정하지 않음)
- id값을 사용해 Friend Entity 객체를 찾음
- 성공적이었다면 ResponseEntity객체에 Friend Entity와 Http 상태 코드 200을 담아서 return
- 실패했다면 ResponseEntity의 Header에 BAD_ID라는 이름으로 id값을 담고 Http 상태 코드 404를 담아 return
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Friend> getFriendById(@PathVariable int id) {
ResponseEntity<Friend> entity;
try {
Friend f = friendR.findById(id).get();
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(f, HttpStatus.OK);
} catch (Exception e) {
HttpHeaders header = new HttpHeaders();
header.add("BAD_ID", "id");
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(header, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
return entity;
}
결과
실패(존재하지 않는 id값을 보낸 경우)
성공
클라이언트에서 JSON 형식으로 전달된 데이터를 Friend 테이블에 저장하는 메서드를 구현한다. 이 땐 ID 외의 데이터만 전달한다. – POST 방식
- @PostMapping 사용
- 파라미터들을 @RequestBody를 사용해 Friend 커맨드 객체로 받아 저장
- id의 경우 자동으로 생성되기 때문에 (auto increment)
- FriendRepository의 save()를 호출하여 저장
- 실패할 경우 "실패했습니다." 문구와 HTTP 상태코드 500을 리턴
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<String> register(@RequestBody Friend vo) {
ResponseEntity<String> entity;
try {
friendR.save(vo);
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.CREATED);
} catch (Exception e) {
entity = new ResponseEntity<>("실패했습니다.", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
return entity;
}결과
성공
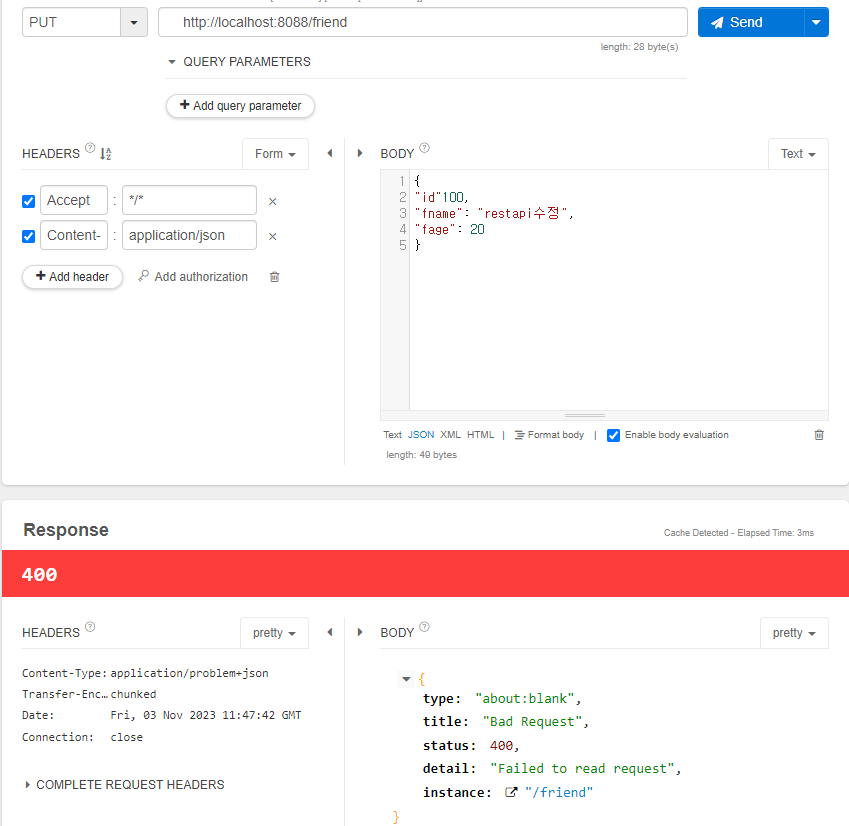
클라이언트에서 JSON 형식으로 전달된 데이터를 Friend 테이블에 저장하는 메서드를 구현한다. 이 때는 ID 도 전달해야 한다. – PUT 방식
- @PutMapping
- 파라미터를 통해 받은 Friend vo에서 id를 추출해와서 Friend 엔티티 객체를 찾음
- 찾아온 f에 파라미터로 받은 것들을 set시킨 뒤 save()시킴
- 성공과 실패 여부에 따라 Body와 HttpStatus에 값을 저장한 뒤 return
@PutMapping
public ResponseEntity<String> update(@RequestBody Friend vo) {
ResponseEntity<String> entity;
try {
Friend f = friendR.findById(vo.getId()).get();
f.setFage(vo.getFage());
f.setFname(vo.getFname());
friendR.save(f);
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.RESET_CONTENT);
} catch (Exception e) {
entity = new ResponseEntity<>("수정을 실패했습니다.", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
return entity;
}
결과
실패(존재하지 않는 id값을 보낸 경우)
클라이언트에서 전달된 ID 를 가지고 데이터를 삭제하는 메서드를 구현한다. – DELETE 방식
- id값을 사용해 Friend 엔티티 객체를 찾은 뒤 delete()를 사용해 삭제
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<String> delete(@PathVariable int id) {
ResponseEntity<String> entity;
try {
Friend f = friendR.findById(id).get();
friendR.delete(f);
entity = new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.RESET_CONTENT);
} catch (Exception e) {
entity = new ResponseEntity<>("삭제를 실패했습니다.", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
return entity;
}
'Spring Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [error] lombok annotation handler class lombok.eclipse.handlers.handlesuperbuilder failed 에러 해결 방법 (0) | 2024.06.24 |
|---|---|
| Error io.jsonwebtoken.lang.UnknownClassException (Maven 방식) (0) | 2023.08.07 |
| 회원가입 기능 구현 (2) | 2023.07.17 |





댓글